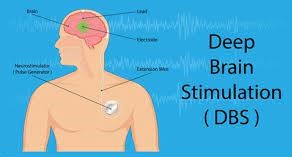
Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS (deep brain stimulation) is a type of operation to insert a device that sends electrical signals to brain area responsible for body movement.
DBS (deep brain stimulation) is a type of operation to insert a device that sends electrical signals to brain area responsible for body movement. Electrodes are made to be placed deep inside the brain area and are connected to a stimulator device. It is very similar to a pacemaker which is placed in the heart, a neurostimulator uses electrical pulses to regulate the brain activity.DBS can help reduce the symptoms of tremors, slowness of movement by the body, stiffness and walking problems caused due to Parkinson’s disease, dystonia or essential tremor. When the stimulator is successfully implanted it allows people to better manage their symptoms, reduce medication and improve quality of life.
What happens before the surgery?
There are several tests that you have to do before the surgery. The test includes a blood test, electrocardiogram, chest X-ray etc. the MRI scanning of your brain will also be performed. You have to inform the doctor about your medical history, including allergies, medicines, anesthesia reaction and previous surgeries.
What happens during the surgery?
Stage 1: attach stereotactic frame
The procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head area. While you are yet seated the frame is made to temporarily position on the head with Velcro straps. The four-pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize the discomfort and pain. You might feel some pressure as the pins are tightened.
Stage 2: MRI or CT scan
You will now have an imaging scan using either computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A box-shaped device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help the surgeon to pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI/CT images and special computer software to plan the route of the electrode.
Stage 3: skin and skull incision
You will be finally shifted to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any minor movements of your head while inserting the electrode. You will remain awake during the surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then gradually it is stopped so that you can talk to the doctor and perform tasks.
The hair is shaved about an inch wide incision line. A skin incision is made across the top of your head to expose the skull inside. Using drill two quarter sized burr holes are made on the left side and right side of the skull. These holes are a passage for the electrodes to pass through the brain.
Stage 4: Insert electrode in the brain
Through these small holes recording electrodes are inserted one by one. Based on the calculation of the imaging produced from the MRI or CT scans and planning computer, the electrode is inserted to a precise depth and angle inside the brain. The brain itself does not feel the pain, so there is no discomfort to the patients.
The accuracy of the electrode placement is confirmed by numerous tests. You will be asked to lift your arms, legs or count numbers. The recording electrodes can here the brain cells firing and display the wave formed on the computer. It is repeated for both left and right side of the brain.
Stage 5: Stimulate the brain cell
Once the exact nerve cells are located the surgeon replaces the recording electrode with permanent DBS electrode. The test is again performed.
Stage 6: closure
When the team is satisfied with electrode placement, a plastic cap is placed over burr hole to hold the electrode in place. A coil of wire is left under the scalp for later attachment to the stimulator. The scalp is closed with sutures or staples and bandage is applied.
